UX Metrics Guides

Introduction
Hey there, design enthusiasts! Ever wonder what makes your favorite apps, websites, and products so cool? It’s not just about looking pretty; there’s a whole science behind it! Think of design like baking the perfect cake — there’s the recipe (metrics), taste-testing (testing), and adding those special ingredients (additional topics). But don’t worry, we’re here to make it as easy as pie (or cake). So, grab a seat and get ready to dive into the world of design with us — it’s gonna be a blast!
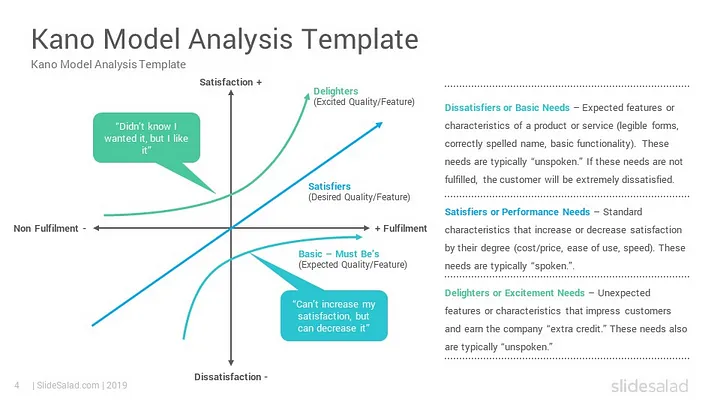
What is metrics?
UX metrics are like checking if your digital cake (app, website, product) is delicious and easy to eat. They reveal how users interact with it, showing if they find what they need easily, enjoy the experience, and even come back for more. By measuring things like time spent using it, task completion ease, frustration levels, and user feedback, you can see what works well and what needs improvement. Just like tasting your cake, UX metrics help you create a delightful digital experience that people love to use.
Types of metrics
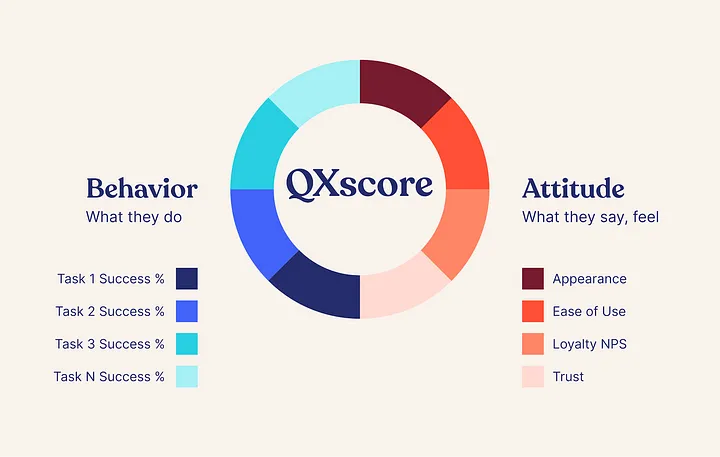
Introduction
1. Behavioral Metrics:These metrics focus on how users actually interact with the product, revealing their actions and behaviors. They provide insights into usability and efficiency.
- Task Success Rate: Measures the percentage of users who successfully complete a specific task within the product. Formula: (Number of users who successfully completed the task) / (Total number of users who attempted the task) * 100
- Time on Task: Measures the average time it takes users to complete a specific task. Formula: (Total time spent on the task by all users) / (Number of users who attempted the task)
- Clickstream Analysis: Tracks the sequence of clicks users make within the product, revealing their navigation patterns.
- Heatmaps: Visualize areas of the interface that receive the most user attention.
2. Attitudinal Metrics:These metrics capture users’ perceptions and feelings about the product, revealing their emotional responses and overall satisfaction.
- ustomer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measures user satisfaction with the product through direct surveys or feedback forms. Formula: (Number of users who responded positively to the satisfaction question) / (Total number of users who responded) * 100
- System Usability Scale (SUS): Measures perceived usability of the product through a standardized questionnaire.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): Measures the perceived effort required for users to complete tasks within the product
3. Engagement Metrics:These metrics measure how long users interact with the product and how deeply they engage with its features.
- Unique Visitors: Tracks the number of individual users visiting the product.
- Returning Visitors: Tracks the number of users who visit the product repeatedly.
- Pageviews: Tracks the total number of pages viewed by users.
- Time on Page: Measures the average time users spend on a specific page. Formula: (Total time spent on a specific page by all users) / (Total number of pageviews for that page).
- Scroll Depth: Measures how far users scroll down a page.
Quantifying Success : Design Metrics in Action
Design metrics act as the measuring instruments in the design process, enabling us to objectively assess the effectiveness of our design decisions. By tracking key performance indicators, we gain a clear understanding of how users interact with our product and identify areas for improvement.
- Conversion Rate: This metric measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase on an e-commerce website or signing up for a service. A high conversion rate indicates the design is effectively guiding users towards the intended goal.
Real-life Example: A company revamps its website, aiming to increase online sales. By analyzing website traffic data and conversion rates, they discover a significant drop-off in the checkout process. User behavior analysis reveals confusing form elements and a lack of clear calls to action. Based on these insights, the design team streamlines the checkout flow and optimizes the layout, leading to a significant increase in conversion rates.
- Engagement Metrics: These metrics measure how long users interact with a product, such as average time spent on a specific page or the number of scrolls within a mobile app. High engagement indicates that users find the design interesting and informative.
Real-life Example: A news organization observes a decline in user engagement on their mobile app. Analyzing engagement metrics reveals users are quickly scrolling through articles without fully reading them. The design team implements a “Read Later” feature and optimizes the article layout for better readability, resulting in longer engagement times and a more immersive reading experience.
- User Satisfaction Surveys: While quantitative metrics provide valuable insights into user behavior, qualitative feedback through surveys and user testing sessions is crucial for understanding user sentiment and identifying areas of improvement that might not be evident through numbers alone.
Real-life Example: A bank implements a new interface for its online banking platform. User satisfaction surveys reveal that customers find the interface confusing and the navigation cumbersome. Based on this feedback, the design team revisits the layout, simplifies the navigation structure, and provides clearer visual cues, leading to improved user satisfaction and a more intuitive banking experience.
Testing : Ensuring a Seamless User Journey
Just as a chef meticulously tests their dishes before serving them, user testing is an essential component of the design process. It involves simulating real-world user interactions to identify and address any usability issues that might hinder the user experience.
- Usability Testing: This involves observing real users interacting with a product to identify any usability problems. By observing user behavior and collecting feedback, designers can pinpoint areas of confusion, frustration, or inefficiency within the design.
Real-life Example: A company revamps Real-life Example: During usability testing for a new e-commerce platform, the design team observes users struggling to locate specific product categories within the navigation menu. Based on these observations, the team reorganizes the navigation structure and implements clearer category labels, resulting in a more intuitive and efficient shopping experience.
- Accessibility Testing: This ensures that the design is usable by people with disabilities. By incorporating accessibility best practices and conducting thorough testing, designers can create products that are inclusive and cater to a broader range of users.
Real-life Example: A news organization Real-life Example: A government agency redesigns its website to provide better access to public information. Accessibility testing reveals that the website is not compatible with screen reader software used by visually impaired individuals. The design team implements changes to improve the website’s accessibility, ensuring equal access to information for all users.
Beyond Metrics and Testing : The Human Touch
While design metrics and testing provide valuable tools for building successful products, it’s crucial to remember that design is ultimately a human-centered endeavor. It involves empathy, creativity, and a deep understanding of human behavior.
- Emotional Design: Great design evokes emotions. It can make users feel happy, excited, secure, or inspired. Understanding the emotional impact you want to create with your design and tailoring your approach accordingly is essential for building a product that resonates on a deeper level.
- Storytelling: Every design tells a story. What message do you want to convey? How can you use visual elements, interactions, and content to create a compelling narrative that engages users and leaves a lasting impression?
- Continuous Iteration: Design is rarely a one-shot process. Be prepared to iterate and refine your designs based on user feedback, changing trends, and evolving needs. Continuously testing, gathering feedback, and making adjustments ensures that your product remains relevant and delivers an exceptional user experience over time.
UX Measurement Framework
1.AARRR Framework: This popular framework focuses on key metrics throughout the customer lifecycle:
- Acquisition : How users discover and start using the product.
- Activation : How users have a positive initial experience and become engaged.
- Retention : How users continue to use the product over time.
- Referral : How users recommend the product to others.
- Revenue : How user behavior translates into financial gains.
2.RARRA Framework : This framework prioritizes retention over acquisition, acknowledging the importance of keeping existing users happy.

Customer Experience (CX) Frameworks:
- CX Index : This framework focuses on measuring customer loyalty and its impact on revenue. It uses two key metrics:
- CSAT (Customer Satisfaction) : Measures user satisfaction with the product or service.
- NPS (Net Promoter Score) : Measures user loyalty and willingness to recommend the product.
User-Centered Design Framework:
This framework focuses on user emotions and their interaction with the product:
- Happiness : Measures user satisfaction and emotional response to the product.
- Engagement : Measures how much and how often users interact with the product.
- Adoption : Measures the rate at which new users acquire the product.
- Retention : Measures how many existing users continue using the product over time.
- Task Success : Measures the percentage of users who successfully complete their desired tasks.

Conclusion :
Crafting exceptional products is like baking the perfect cake: it requires the right recipe (metrics), careful testing, and a dash of human magic. Metrics act as your measuring tools, revealing how users interact with your design and what needs improvement. Testing, like taste-testing, ensures a smooth user experience by identifying and fixing any usability issues. But don’t forget the human touch! Great design goes beyond functionality; it considers user emotions, tells a compelling story, and continuously adapts based on feedback. By embracing these elements, you can create products that not only work well but also leave a lasting positive impression on the people who use them. Remember, design is a journey, so keep testing, learning, and iterating to make your product truly delightful and user-friendly.